Untrue & Debunked
With years of experience, we’d say we’re experts in direct mail marketing. But we’re not just the mail people. We provide highly impactful direct mail marketing that cuts through today’s digital noise to deliver a tactile experience and leave a lasting impression. That’s why we’re well versed in all of the misconceptions about direct mail floating around out there, and can tell you exactly why they’re untrue. Follow along as we debunk the 6 misconceptions of direct mail.
Misconception 1: Direct mail is past its heyday
Once in a while, we hear people speculate and assume that direct mail is past its peak – but just because direct mail has stood the test of time, doesn’t make it outdated. It’s been around for a while for a reason, and has evolved and changed over time – with the times. In fact, in a recent IAB survey, six out of ten marketers prefer direct mail over other offline channels and still include it in their direct marketing strategy today.
These days, direct mail breaks through the digital noise and is unique and different than other marketing tactics. It brings about nostalgia, as people enjoy the feeling of paper in their hands, similar to enjoying paperback books over kindles. Plus, for every 36 emails you receive (on average), you get 1 piece of mail in your mailbox. The possibilities are quite endless, with many exciting design opportunities and options. Really, direct mail is only boring and old if you make it that way.
Misconception 2: Compared to other tactics, direct mail doesn’t provide ROI
This one couldn’t be further from the truth. Don’t believe us? Here are just a few stats to back us up. The average lifespan of an email is 17 seconds, compared to direct mail’s average lifespan of 17 days. Up to 90% of direct mail gets opened, compared to only 20-30% of emails. Per USPS, 98% of people check their mail daily and Americans spend upwards of 30 minutes with their mail on a single occasion. Direct mail open rates can reach up to 42%. Recipients of direct mail also “purchase 28% more items and spend 28% more money than people who don’t get that same piece of direct mail.” Direct mail gets response rates 10 to 30 times higher than digital channels, according to the DMA (Direct Marketing Association).
Basically, direct mail usually does very well in terms of ROI, and it can (and should) be tracked – so make sure you’re getting the most out of it by making it trackable with the use of digital touchpoints.
Misconception 3: Direct mail marketing is expensive
When people think of print, they sometimes think of high-cost, but that’s not always the case. If you have a quality list and are getting the most out of each mailer you send, direct mail won’t seem all that expensive. What do we mean by a quality list? If you’re sending to strategic, particular contacts – not just any contacts, your ROI will be worth the price.
Additionally, print often gives you more for your money while other marketing practices alone may not (for example PPC, social media ads, email marketing platforms, and more). According to the stats, mail marketing is much more likely to be seen and paid attention to.
Misconception 4: Millennials and younger don’t like or pay attention to direct mail
Direct mail isn’t just effective for older audiences. Actually, 73% of American consumers (in general) say they prefer being contacted by brands via direct mail because they can read or review the information at their leisure. And, 41% of Americans of all ages look forward to checking their mail each day.
Millennials, specifically, like to feel important and seen, so the personalization opportunities of direct mail make for great millennial marketing. To add to this, many millennials and Gen-Z-ers have digital fatigue and find taking a “break” with print to be often enjoyable, and it “should be no surprise that those raised on the internet are best able to tune out online ads.” They also have shown to have a lot more trust in print resources than in digital.
Misconception 5: Direct mail works on its own and doesn’t integrate with other channels
These days, direct mail is actually an excellent touchpoint among many, especially when conducting a multichannel marketing campaign. And, we’d even say that combining tactics, even if it’s just two, is usually the way to go. In a recent study, a whapping 68% of marketing respondents saw that combining digital and direct mail increased visits to their websites.
So, how do you integrate physical with digital? By using a URL of a landing page or website, a PURL (personalized URL), BRC (business reply card), or a QR code. Any of these can be used to lead the viewer to a digital touchpoint. These can all also be used to measure attribution and better understand your target audience, and the emails and other information acquired from BRCs or online landing page forms can be used for email marketing, targeting customers with digital advertising, and sending further communication.
Misconception 6: Direct Mail = Junk Mail
Unlike junk mail, direct mail is focused, targeted, relevant, ROI-producing, and uses a quality send list. For more on why direct mail isn’t the same as junk mail, check out our blog, “Direct Mail vs. Junk Mail”, here. Strata can be a resource for direct mail with a surgically targeted list of prospects that are not only more likely to have a need for your project or service, but are also more likely to respond.
Now that it’s a bit clearer that direct mail is relevant, effective, and can be a huge part of the bigger picture of a marketing strategy, you may be interested in giving direct mail marketing or multichannel marketing a try. If so, give us a call.
How to Fight it & Flourish
As spooky season approaches and Halloween is around the corner, we’re thinking a lot about our biggest fears. But today we’re not talking about ghosts or goblins or even Michael Myers. We’re talking about one of the scariest things of all to any workplace…complacency.
“Complacency is man’s biggest weakness. It creeps up on us when we least expect it.” – Jay Mullings
Even if you think your company isn’t anywhere near complacency, there’s still always room to evaluate and grow. And, you may be surprised by what’s lurking behind the door of contentment. Complacency is not only bad for your company, but good for your competition, which we’d assume will give you a bit of a fright. If employees aren’t challenged to improve, things are the way they are because it’s the “way they’ve always been”, and the company isn’t growing, it’s definitely affecting your revenue. But don’t worry – it’s never too late to change. In this blog, we’ll take a look at the best ways to avoid company complacency and ensure you’re periodically updating and enhancing your culture, practices, and marketing.
Complacency’s Cause
Complacency can sneak up on any company without warning, shielding it from growth and stifling creativity and innovation. Why? Because if companies are seemingly doing “fine” and meeting their goals on paper, they feel no “need” or urgency to change. That’s where the biggest mistake is made, because companies should always be looking to evolve and thinking about their vision for the future. If not, ideas become stale, talent becomes bored, and eventually, the company comes to a jarring halt without any clue of how they got there.
When everything seems to be going well, it can be difficult to disrupt successes. And it may feel like the right decision to let processes and practices take their course rather than think about next steps and development, but often “the riskiest thing we can do is just maintain the status quo.” Without urgency and consistency for change, employee performance shifts and can even decline. Statistics show that only 30% of employees in America are actually engaged in their work, and only 13% of employees worldwide are engaged in their office environment. With such low numbers already, it’s so important to keep employees excited, energized, and motivated for what they’re doing and what’s to come.
Combatting Complacency
With complacency being a bigger, scarier possibility than you may have assumed, it’s important to keep it top of mind and to make sure you’re doing your best to combat it. Start with communication of your company’s mission, vision, and values. Make sure they’re clear, known, and maybe most importantly – accurate and true. Know who you are. If you do – your employees will too, and in turn they’ll feel more connected with and motivated by your workplace. Allow employees to see their contributions to the bigger mission, and their worth as an asset to the overarching vision.
After all, having a good (and growing) company culture is key to combatting complacency and ensuring workplace satisfaction. How do you improve your culture? Many ways, but the most effective tools are company newsletters, employee highlights, group meetings, and employee appreciation. Again – make your employees feel valued, and they’ll more likely provide value.
Additionally, make sure team members feel important and part of the greater whole. Encourage managers and team members to communicate within their individual teams, and make sure responsibilities are delegated and well distributed. Employees are more likely to become bored when they’re doing the same tasks over and over, so give them room to be creative and explore new opportunities. You never know who may have the next best idea.
Lastly, be prepared for whatever may come your company’s way, and never be too afraid to challenge the status quo. If we’ve learned anything these past two years, it’s that anything can happen, and that the saying “it won’t happen to us” is just not realistic. It’s important to listen to the ideas of your employees and always be prepared for what’s to come with an open communication structure. Make sure you have multiple decision makers, not just one, and that employees feel comfortable enough to make some decisions without “permission” from a leader. Training your employees to make decisions on their own will be a key factor in combatting complacency.
Refreshing Without Fear
Almost as important as your workplace and its people is your brand and marketing. Without change and evolution, your marketing can quickly become out-of-date right under your nose (causing your employees to lack company pride and your audience to lose interest). But how do you know when it’s the right time to update your brand and marketing?
A sure sign (these days) of lack luster marketing is an absence of social platforms. Some would even say if you’re not online, you might as well not exist. And although we think that sounds a little spooky, we’ll admit that it holds some truth. If you’re hard to find and not posting relevant content and imagery, target customers may be choosing your competitors (who are more accessible and approachable) over you.
Also important to your brand and its relevance is your website. In this day and age, it’s very easy to tell when a website has been left alone so long that it’s developing cob-webs. If you’re finding that your website traffic is down and your customers aren’t interacting with it, it’s time for an upgrade. But, before any big changes, compile data and make purposeful decisions. What is your audience looking for? What do they respond well too? How can you quickly and easily get them to have interest in your company and purchase goods?
Additionally, make sure you keep your advertising and customer communication – whether digital or physical – energized and creative. Combine direct and digital marketing to reach specific audiences and keep your brand top of mind. Don’t settle for just one medium that “seems to be working” if multiple channels of communication could bring you more success.
Lastly, avoid complacency by focusing on helping the customer rather than selling to them. While the overall goal of most companies is to generate sales, it’s essential you show your customers that you care about their pain points and needs. To see all of these tactics in action, check out our recent blog on how to create successful marketing campaigns.
Company complacency can sneak up on you like a ghost in the night and lead to missed opportunities, poor customer service, and disengaged employees. Stay aware of the possibility of contentment and make sure you’re always exploring, evolving, and rising above the rest. Change is inevitable, but complacency doesn’t have to be.
For more information on what we do at Strata and how we can help you fight complacency with one of our marketing solutions, contact us today.
With the Top 10 (Other) Best Rebrands & Refreshes
We can’t believe we’re already celebrating the one-year anniversary of Strata’s brand refresh. It’s been quite a year (to say the least). But we can honestly say that, with all of the struggles of 2020-2021, our brand refresh wasn’t one of them. If it did anything (and it did a lot), it definitely brought us together, made us more confident, and better showcased our personality, vision, team, and solutions. The brand refresh catapulted Strata into 2020, helping us solidify our style and services, attract new talent, and stay inspired.
When we decided we needed a new look – we had to pick between a full rebrand or a refresh. For us, the answer was easy. A complete rebrand would have required scrapping our identity and starting from scratch, where a refresh allowed us to keep our main identity and strategy intact. Our brand was strong with our current clients and we had a great reputation as problem solvers and solutions experts – so a refresh was perfect for what we needed to do.
With any rebrand or brand refresh – “consistency across all channels is key”. Over the past year, we’ve ensured that all our materials – from website to print, are on-brand.
Since we now have a bit of rebrand and refresh experience under our belts, we wanted to take a look at the top 10 best company rebrands and refreshes (in our eyes) besides Strata’s, of course.
Our Top 10
Dropbox
Dropbox refreshed its brand in 2017, and it was nothing short of successful. The company worked with design studio “Collins” to create a cleaner and simpler logo and lots of illustrative elements to better connect with their primarily creative and collaborative audience.
Airbnb
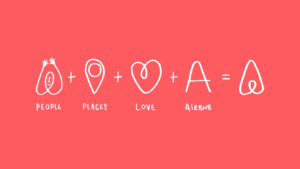
Airbnb did a full rebrand in 2014 with Design Studio, sending their team of designers to 13 cities to truly immerse themselves in Airbnb’s offerings, community, and mission. It resulted in a beautiful brand that differentiated Airbnb from its similar competitors. The CEO of Airbnb even stated, “When I look at this brand, I suddenly realized everything I’ve been trying to say, now we have a way to express it.”
Walmart
“There are very few companies in the world that managed to change the public perception of their brand as successfully as Walmart did.” In 2008, Walmart made this change to get away from their “always low prices” slogan that often-made customers feel like it was also “always low quality”. They also wanted to steer clear of the questionable corporate practices they were called out for in the early 2000s. So, Walmart did a complete 360 with a whole new brand from redesigned stores to a new look and personality.
Southwest
We love this brand refresh because it reminds us of ours. Without a complete overhaul, Southwest changed its look and logo to showcase their humanity and heart – literally.
Guinness
Good old Guinness. Many love it, others don’t, but it always holds true that Guinness makes us feel like we’re back in the olden days, sipping a brew in the pub. Instead of following the crowd of flat logo designs, Guinness actually added detail to its logo in 2016, working “with real harp makers to breathe new life into the legendary logo” that “could be built into an actual harp that would work properly and be in tune.”
Starbucks
Starbucks is loved by many – and dare we say it – is mainly successful because of its brand (although we do love it a latte). They’ve made slight changes over time to the brand, always increasing their user experience and recognizability with a “distinctive color scheme, typography, and illustrations.”
Taco Bell
You may not have really noticed Taco Bell’s brand refresh until now – but its cleaner, simpler look has helped it stay relevant among its many fast food and taco chain competitors. Along with this well-done refresh, Taco Bell has been named “one of the healthiest fast-food chains in America,” so, they’re doing quite well.
Mastercard
In 2016, Mastercard conducted a refresh with Pentagram to emphasize “simplicity, connectivity and seamlessness.” It’s simple and sleek look of just the famous two overlapping circles is surprising, but logic-based. “The change follows research by Mastercard that found that more than three quarters of people asked were able to identify the brand from the two interlocking circles alone.
Burger King
For the first time in 20 years, Burger King conducted a brand refresh with a new logo, uniforms, and packaging – and we love its nostalgic look. The new logo is actually very close to BK’s logo design from the 70s-90s. The creative agency on the project wanted to “pay homage to the brand’s heritage with a refined design that’s confident, simple and fun.”
Intel
Last but not least, Intel’s 2020 refresh caught our eye because of its subtle hints to past logos. Again, it refers back to their past while being currently relevant. “This new logo includes elements of both (past logos), but in a much more subtle, minimalist way.”
To take a more in-depth look back at our brand refresh, visit our original refresh blog, here. If you’re looking to make your branding and marketing communications more effective and efficient, give Strata a call.
Get to Know These Tracking Treats
Within the world of marketing, there’s a lot of buzz around the topic of cookies and what the future holds for tracking website visitors and generating personalized advertisements. While the topic’s relevant, not many people are completely informed on what cookies are and the impact they have on our ability to create better customer experiences. In this blog, we’re going over what cookies are, the differences between first-party and third-party cookies, and the future of online tracking.
So, What Are “Cookies”?
Although many of us are “foodies” here at Strata, and could talk about a good dessert all day, this blog isn’t about Oreo or Chips Ahoy. We’re talking about web “cookies” – text files put into a user’s browser page while they’re visiting a website. Cookies are known by several names – web cookie, internet cookie, browser cookie, or HTTP cookie, but they’re all the same, and in general, they track and log browsing activity against identification data such as IP addresses. Why is this information useful? Primarily, cookies help save information about a user in order to personalize their website experience and the advertisements they’re shown.
While cookies have enjoyed a childhood free of regulation, their “free-willy” time is coming to an end with recent regulatory initiatives driven by an increase in public concern over internet privacy. The first major change came when General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) made consent mandatory in order to track visitors on a website. To give you a feel for the impact of GDPR – about 11% of users click to “accept all cookies”, 76% of users ignore the banner completely, 12% close the cookie banner, and 0.5% of users actually open up cookie settings, read through terms and agreements, and sometimes make adjustments. These numbers are misleading, however – what GDPR essentially did was force the user to choose between viewing the desired content and accepting cookies OR (with exceptions) leaving the site entirely. So, while it looked good – almost all of the visitors in the stats above were still being tracked.
At this point, you might be thinking that we need to eradicate the cookie – if so, hold that thought. Cookies almost always make your experience on the web better – they’re your friend, not your enemy. To solve privacy concerns – which is the intent of all privacy-centric regulation – we’ll need to jump down a level. There are two major types of cookies – First-Party and Third-Party. Both contain the same pieces of data and technically can conduct the same actions, but they’re created differently, used differently, and have different benefits for distinctive situations. Let’s get into each one.
First-Party Cookies
Simply put, first party cookie technology is usually installed or authorized by a website’s owner and only tracks that user across that specific website. First-party cookies are set on the publisher’s server or on the JavaScript loaded to the website. Their defining technical feature is that, for the most part, only the domain that created the cookie can access it, thus they are seen as less invasive and are more welcomed by users.
These cookies allow website owners to collect analytical data, remember individual user settings or content (remembering what’s in a user’s shopping cart, their language preferences, or their username and password), and perform useful functions to provide better user experience. That last part is important – first-party cookies primary purpose is to deliver more relevant, user-friendly experiences to individuals. If you’d like to see the difference they make, just clear your browser cache and visit some of your favorite websites.
Third-Party Cookies
Contrasting first-party cookies, third-party cookies are not created by the domain of the website the user’s currently visiting, and therefore, can often seem intrusive and un-welcomed. This type of cookie is placed by another site, such as an advertiser or social media platform like ad.doubleclick.net – and is separate from the home domain. These cookies are usually used for online advertising purposes, and are added through a script, code, or tag to track a user across several websites. Enabling these cookies can help users see relevant discounts and catered advertisements, but can also possibly involve them in a breach of privacy. For this reason, third-party cookies are blocked by many browsers, and are currently being chastised as unethical.
Phase Out of Third-Party Cookies
In February of 2020, Google announced its phase out of third-party cookies by 2022. When this occurs, it will cause 56% of web browsers (the percentage that use Google Chrome) to block their use automatically. As stated by Google, their reasoning for forcing this phase out is to increase security and protect the user. You have to wonder, however – are ethics the driving principle here, or is this a strategic move to further corner the digital advertising market?
All-in-all, this change won’t make as much of a difference as you’d think, as a 2017 study showed that 64% of tracking cookies were already being blocked as users surfed the web. Those at Google seem to think that third-party cookies will not be replaced by another resource due to increasing privacy concerns, but they’ll continue to “support first-party relationships on our ad platforms for partners, in which they have direct connections with their own customers.”
What’s Next for Cookies?
No matter what the circumstances with third-party cookies, first-party cookies are definitely here to stay. If configured correctly, they’ll continue to function within most browsers – even if those browsers block third-party cookies. So – fear not – first-party cookies will provide marketers hindsight and insight on your website visitors for the foreseeable future – even if you might now be forced to use Google to reach them.
Now that you know a bit more about cookies, you may be motivated to improve and optimize your next digital marketing campaign. If so, contact us today.